In previous article, we have written tutorial about how to fix SQL Collation conflict in SQL server. In this article, we are going to understand SQL Server error: The Primary filegroup is full and how we can fix this error.
The database administrators must keep track of the database growth. Also, they must do the capacity planning and space management according to the growth and utilization of the database. When we create a new database, we set the value of the max size parameter to UNLIMITED most of the time. However, sometimes due to business requirements and hardware constraints, we are forced to keep the value of the MAXSIZE parameter to a specific value.
When we set the value of the MAXSIZE parameter limited to a specific value, we might encounter the Primary filegroup is full error. This error also occurs when we are using the SQL Server express edition. The maximum allowed size of the database in SQL Server Express edition is 10GB. When the database tries to grow beyond 10GB, the user will encounter the Primary filegroup is full error.
To understand the concept and error, we must create a demo setup with a specific configuration. I have created a database named DemoDatabase, and the size of the database is 40MB. Run the following query to create the database.
CREATE DATABASE [DemoDatabase] ON (NAME = N'DemoDatabase', FILENAME = N'C:\MS_SQL\Data\DemoDatabase.mdf' , SIZE = 2048KB , MAXSIZE = 20480KB ) LOG ON (NAME = N'DemoDatabase_log', FILENAME = N'C:\MS_SQL\Log\DemoDatabase_log.ldf' , SIZE = 2048KB , MAXSIZE = 20480KB ) GO
USE [DemoDatabase] GO CREATE TABLE tblFilegroup(first_name varchar(500), Address char(8000)) GO
INSERT INTO tblFilegroup VALUES ('Nisarg','AB-14, Akshardham Flats, Urban bank road, mehsana') GO 5000
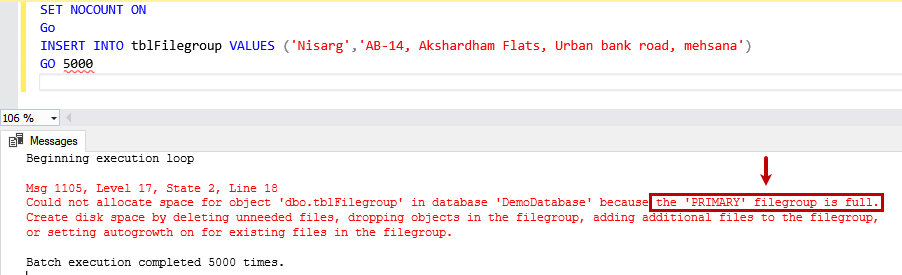
During the execution of the INSERT query, we encounter the following error.
Msg 1105, Level 17, State 2, Line 18
Could not allocate space for object ‘dbo.tblFilegroup’ in database ‘DemoDatabase’ because the ‘PRIMARY’ filegroup is full.
Create disk space by deleting unneeded files, dropping objects in the filegroup, adding additional files to the filegroup, or setting autogrowth on for existing files in the filegroup.
Screenshot:
To identify the root cause, first, let us check the available disk space in the workstation. Run the following command in the PowerShell.
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_logicaldisk -Filter "DriveType = '3'" | Select-Object -Property DeviceID, DriveType, VolumeName, @{L='AvailableSpace';E={"{0:N2}" -f ($_.FreeSpace /1GB)}}, @{L="TotalDiskSize";E={"{0:N2}" -f ($_.Size/1GB)}}
Command Output:
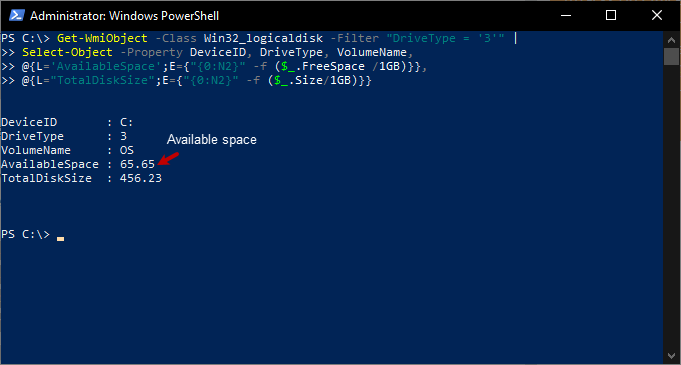
As you can see in the above image, sufficient space is available in the workstation. Now, let us see the value of the MAXSIZE parameter of DemoDatabase. We can query the sys.master_files DMV to review the Autogrowth and max size values of the DemoDatabase. Run the following query.
SELECT databases.name AS [Database Name], materfiles.type_desc AS [File Type], CAST( (materfiles.Size * 8 ) / 1024.0 AS DECIMAL(18, 1)) AS [Initial Size (MB)], 'By '+IIF( materfiles.is_percent_growth = 1, CAST(materfiles.growth AS VARCHAR(10))+'%', CONVERT(VARCHAR(30), CAST( (materfiles.growth * 8 ) / 1024.0 AS DECIMAL(18, 1)))+' MB') AS [Autogrowth], IIF(materfiles.max_size = 0, 'No growth is allowed', IIF(materfiles.max_size = -1, 'Unlimited', CAST( ( CAST(materfiles.max_size AS BIGINT) * 8 ) / 1024 AS VARCHAR(30))+' MB')) AS [MaximumSize] FROM sys.master_files AS materfiles INNER JOIN sys.databases AS databases ON databases.database_id = materfiles.database_id where databases.name='DemoDatabase'
Output
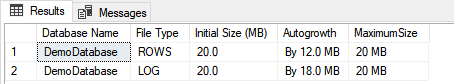
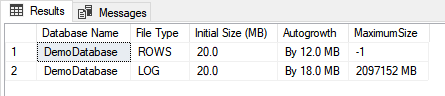
As you can in the above image, the value of the Autogrowth parameter for the data file is 12MB and the log file is 18MB. The maximum allowed size of the data and log file is set to 20MB. To resolve this issue, we can increase the value of the MAXSIZE parameter or set the value to UNLIMITED. In our case, we are going to set the value of the MAXSIZE parameter to UNLIMITED. We can change the values by using any of the following methods.
- Change value using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
- ALTER DATABASE command
First, let us change the value using SQL Server management studio. Launch SQL Server Management Studio -> Connect to the SQL Server instance -> Expand Databases Right-click on Database (we are using database with name below) and click on Properties.
First, we will change the MAXSIZE of data files. To do that, click on Files. In the right pane, click on a balloon in the Autogrowth / Maxsize column in ROWS File Type.

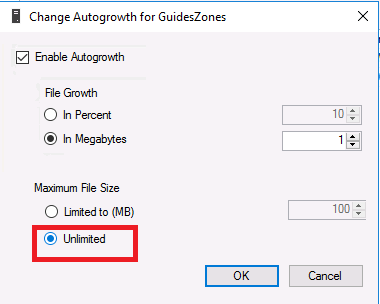
A dialog box named Change Autogrowth for Database above opens. In the dialog box, set Maximum File Size to Unlimited. Click on OK to save the value and close the dialog box.
Alternatively, we can use the ALTER DATABASE statement to change the values of the MAXSIZE parameter. To change the MAXSIZE parameter, the syntax of the ALTER DATABASE statement is the following.
ALTER DATABASE [DB_NAME] MODIFY FILE (LOGICAL_FILENAME, FILEGROWTH= VALUE_IN_KB|UNLIMITED)
We want to set the value MAXSIZE parameter of the data and log files of the Demodatabase to UNLIMITED. To do that, run the following query.
USE [master] GO ALTER DATABASE [DemoDatabase] MODIFY FILE ( NAME = N'DemoDatabase', MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED) GO ALTER DATABASE [DemoDatabase] MODIFY FILE ( NAME = N'DemoDatabase_log', MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED) GO
Once the query is executed successfully, run the below query against sys.master_files DMV.
SELECT databases.name AS [Database Name], materfiles.type_desc AS [File Type], CAST( (materfiles.Size * 8 ) / 1024.0 AS DECIMAL(18, 1)) AS [Initial Size (MB)], 'By '+IIF( materfiles.is_percent_growth = 1, CAST(materfiles.growth AS VARCHAR(10))+'%', CONVERT(VARCHAR(30), CAST( (materfiles.growth * 8 ) / 1024.0 AS DECIMAL(18, 1)))+' MB') AS [Autogrowth], IIF(materfiles.max_size = 0, 'No growth is allowed', IIF(materfiles.max_size = -1, '-1', CAST( ( CAST(materfiles.max_size AS BIGINT) * 8 ) / 1024 AS VARCHAR(30))+' MB')) AS [MaximumSize] FROM sys.master_files AS materfiles INNER JOIN sys.databases AS databases ON databases.database_id = materfiles.database_id where databases.name='DemoDatabase'
Output:
As you can see, the value of the MAXSIZE parameter is -1. According to the Microsoft document, when the MAXSIZE parameter value is -1, the data file can grow until the disk is full.
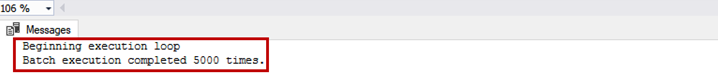
Now, run the following INSERT statement to insert 5000 records. As we have set the value of the MAXSIZE parameter to UNLIMITED, the records will be inserted successfully.
SET NOCOUNT ON
GO
INSERT INTO tblFilegroup VALUES ('Javier','RF-88, New York, Queens')
GO 5000
Output.
As you can see in the above image, the primary filegroup is full error has been resolved and the query inserted 5000 records in the tblFilgroup table successfully.
Summary
In this article, I have explained about the primary filegroup is full error and how to resolve the error. I have also demonstrated a use case to explain when this error can occur and how to fix it and make the database operational.

Javier is Content Specialist and also .NET developer. He writes helpful guides and articles, assist with other marketing and .NET community work