In the world of website management, you will often find yourself in a situation where you own multiple domain names and want one to point to another. Perhaps you’ve acquired a new, more brandable domain for your business, or you’ve registered common misspellings of your primary domain to capture all possible traffic. The question then becomes: what is the best way to make this happen?
The two most common methods to accomplish this are domain forwarding and domain masking.
While they might seem similar on the surface, their underlying technology and, more importantly, their impact on your website’s performance, user experience, and search engine optimization (SEO) could not be more different. In nearly all modern web scenarios, domain forwarding is the correct choice, while domain masking is an outdated practice that can actively harm your online presence.
This comprehensive guide will break down the differences between these two methods, explore their profound effects on your SEO, and provide a clear recommendation on which one you should be using.
What is Domain Forwarding? (The Recommended Method)
Domain forwarding, also known as URL redirecting, is the standard and most common method for sending traffic from one domain to another.
Think of it like a digital “change of address” form filed with the post office. When someone tries to visit your old address (DomainA.com), the server immediately tells their browser, “This content has permanently moved. The new address is DomainB.com.” The user’s browser then automatically loads the new address, and the URL in the address bar changes to DomainB.com.
This process is transparent to the user and is the method that both users and search engines prefer.
Types of Domain Forwarding
There are two main types of redirects, and the distinction is crucial for SEO:
- 301 Permanent Redirect: This is the most important and widely used type. A 301 redirect tells search engines that your page or site has permanently moved to the new location. This is a critical signal for SEO, as it instructs search engines like Google to transfer all the ranking power, authority, and “link equity” from the old URL to the new one.
- 302 Temporary Redirect: This redirect tells search engines that the move is only temporary. This is used in specific situations, such as A/B testing a new page design or redirecting users to a promotional page during a short-term sale. It does not pass the same ranking power as a 301 redirect.
Pros of Domain Forwarding
- Excellent for SEO: A 301 redirect is the correct way to consolidate multiple domains, ensuring that your search engine rankings are preserved and passed to your primary domain.
- Transparent User Experience: Users see the actual URL of the page they are on, which builds trust and avoids confusion.
- Works Perfectly with Analytics: Your analytics tools can accurately track user behavior because each page has a unique, visible URL.
- Bookmarking and Sharing: Users can bookmark or share a link to a specific page on your site, and it will work as expected.
Cons of Domain Forwarding
- Branding is Lost: The only real “downside” is that the original domain name (
DomainA.com) disappears from the address bar, replaced by the new one.
What is Domain Masking? (The Outdated Method to Avoid)
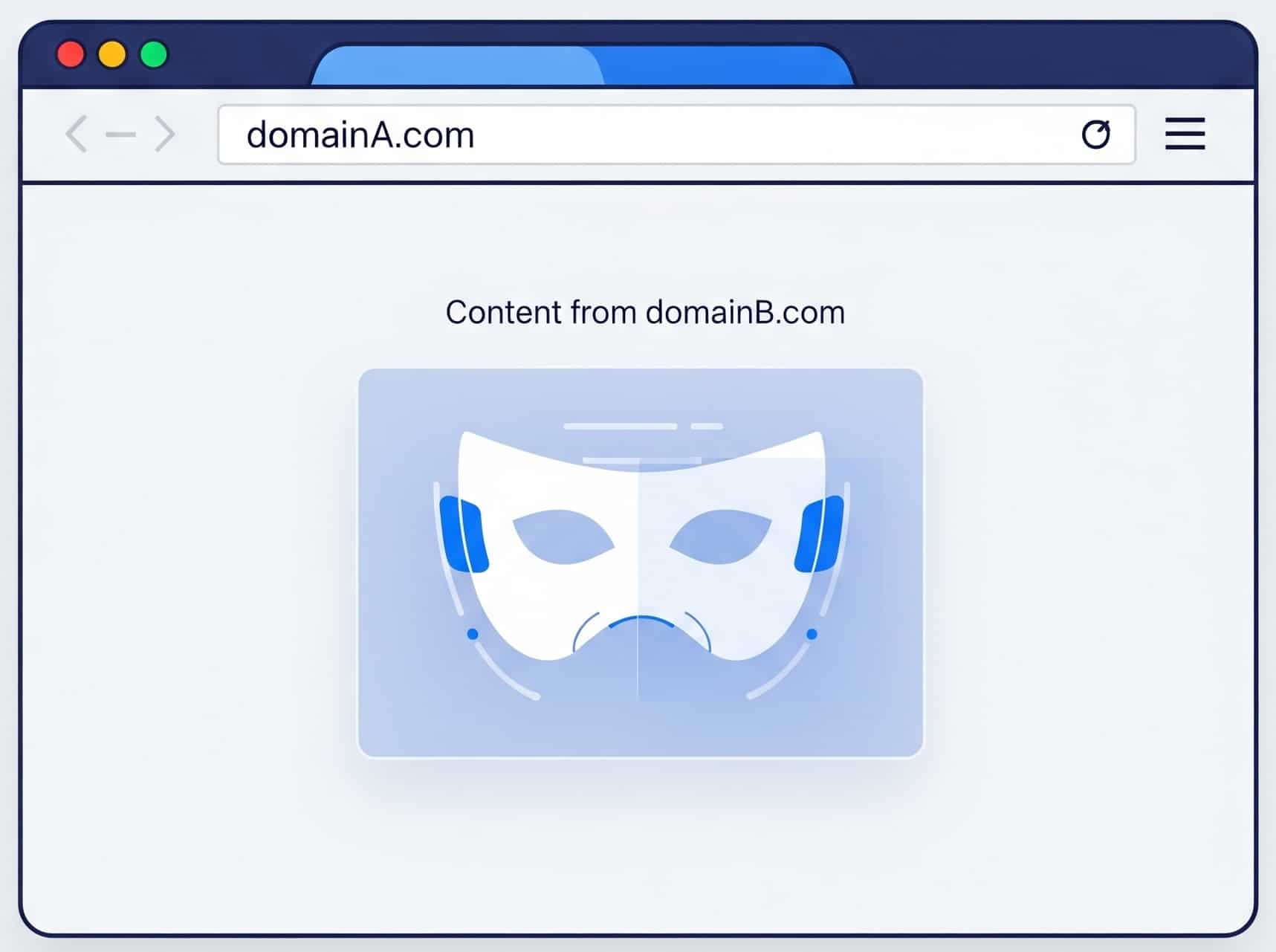
Domain masking, also known as URL masking or URL framing, is an older technique that attempts to display the content of a different website while keeping the original domain name in the browser’s address bar.
Think of it like putting on a mask. Your website at DomainA.com shows the content from DomainB.com, but the URL in the address bar never changes.
Technically, this is usually accomplished by loading the destination website inside an HTML frameset or an iframe. The browser is essentially showing one website inside a window provided by another.
Pros of Domain Masking
- Branding is Retained: The original domain name stays in the address bar. This is the only perceived benefit and the primary reason people used this method in the past.
Cons of Domain Masking (And Why You Should Never Use It)
The downsides of domain masking are severe and numerous, especially concerning SEO.
- Disastrous for SEO: The Duplicate Content Problem This is the most critical issue. When you use domain masking, search engines see the exact same content living at two different URLs (
DomainA.comandDomainB.com). This creates a classic duplicate content problem. Search engines don’t know which version is the “correct” one, so they may:- Split your ranking signals (like backlinks) between the two domains, diluting the authority of both.
- Filter one or both of the domains from the search results to avoid showing duplicate content.
- Become confused and fail to properly crawl and index your pages.
- Poor User Experience
- Broken Bookmarking and Sharing: Because the URL in the address bar never changes, a user cannot bookmark a specific product page or blog post. If they try, they will only ever bookmark the homepage (
DomainA.com). Similarly, if they copy the URL to share it, the link will only ever point to the homepage. - Confusing Navigation: The back button can behave unexpectedly, and the page title in the browser tab will not update as the user navigates through the site.
- Broken Bookmarking and Sharing: Because the URL in the address bar never changes, a user cannot bookmark a specific product page or blog post. If they try, they will only ever bookmark the homepage (
- Security and Display Issues
- SSL Problems: Masking can often break SSL certificates, causing browsers to display security warnings to your visitors.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Content displayed within an iframe may not render correctly or be fully responsive on mobile devices.
Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Domain Forwarding (301) |
Domain Masking (Iframe)
|
| URL in Address Bar | Changes to the destination URL. |
Remains the original URL.
|
| SEO Impact | Excellent. Passes link equity and avoids penalties. ✅ |
Very Bad. Causes severe duplicate content issues. ❌
|
| User Experience | Clear and predictable. |
Confusing and often broken.
|
| Bookmarking/Sharing | Works perfectly. |
Broken. Only the homepage URL is available.
|
| Recommended Use | Almost always. | Almost never. |
How to Set Up Domain Forwarding
To setup domain forwarding at ASPHostPortal, it is pretty simple and quick. Please just follow this steps below
- Log in to your control panel.
- Find the DNS or Domain Management settings for the domain you want to forward.
- Look for an option called “Domain Forwarding,” “Redirect,” or a similar name.
- Enter the full destination URL that you want to forward traffic to.
- Ensure you select the “Permanent (301)” option.
Conclusion
The choice between domain masking and domain forwarding is one of the clearest in all of web management. Domain forwarding, specifically a 301 permanent redirect, is the modern, SEO-friendly, and user-friendly standard. It correctly signals to search engines and users that your content has a new, permanent home.
Domain masking is an obsolete technique that creates significant SEO and usability problems and should be avoided in all modern web development. By understanding the difference and implementing the correct 301 redirect strategy, you can manage your domain portfolio effectively while protecting and consolidating your valuable search engine rankings.

Yury Sobolev is Full Stack Software Developer by passion and profession working on Microsoft ASP.NET Core. Also he has hands-on experience on working with Angular, Backbone, React, ASP.NET Core Web API, Restful Web Services, WCF, SQL Server.



