In these series of posts, we will see how to secure your .Net Core applications.
In this post, we will see how to enforce SSL to your .Net Core applications along with adding HSTS to your .Net production site.
From .Net Core 2.1 onwards, HTTPS is enabled by default in every template which is one of the features of .Net Core 2.1
What is SSL?
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security protocol for establishing encrypted links between a web server and a browser in an online communication
- The usage of SSL technology ensures that all data transmitted between the web server and browser remains encrypted hence secured
To secure your .Net Core applications, you can now enforce the browser to use HTTPS
What is HTTPS?
- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, the protocol over which data is sent between your browser and the website that you are connected to. The ‘S’ at the end of HTTPS stands for ‘Secure’.
- It means all communications between your browser and the website are encrypted.
Let us start.
Prerequisite:
- Visual studio 2017 or Visual Studio 2019 community edition, download here
- .Net Core 5.0 SDK from here
Create the MVC Application using .Net Core 5.0 template in VS 2019
Once you have all these installed, open your Visual Studio 2017 -> Create New Project -> Select Core Web application:
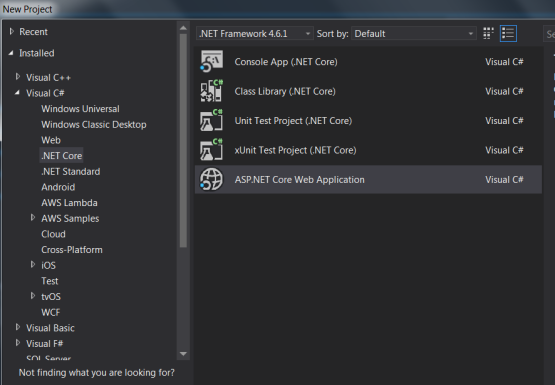
Click on Ok and in next window, select Web Application(MVC) as shown below:
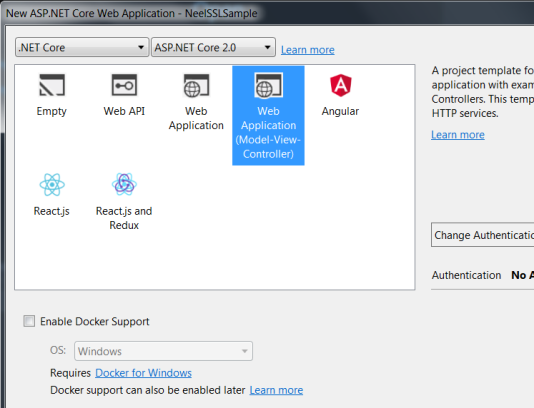
Visual Studio will create a well-structured application for you.
Enforcing SSL on Controllers
Enforcing SSL on Controllers is very easy. You just need to add RequireHttps attribute above the controller:
[RequireHttps]
public class HomeController: Controller
{}
Enforcing SSL globally
As you might have so many controllers and with Controller enforcing you need to make the changes in so many controllers. There is a different approach where you can enforce the SSL globally by making changes in Startup.cs class.
Add below lines in the ConfigureService method:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
services.Configure(options =>
{
options.Filters.Add(new RequireHttpsAttribute());
});
}
Above code requires all requests to useHTTPS therefore HTTP requests are ignored.
Side Note: Enforcing SSL globally is a good practice and more secure than adding attributes on the controller level. Even if new controllers are added, you would have a headache to add the attributes above all new controllers.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Applications typically need to listen to both HTTP and HTTPS but then it is required to redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
Add below code in Configure method in Startup.cs class which will redirect all HTTP calls to HTTPS:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
var options = new RewriteOptions()
.AddRedirectToHttps(StatusCodes.Status301MovedPermanently, 63423);
app.UseRewriter(options);
app.UseMvc();
}
That is it.
Run above application on IIS Express
Please note that if you will run above application on IISExpress then it will throw an error.
This error comes because you have not yet configured your IIS Express settings to allow SSL. You need to Enable SSL.
For that open the properties of the application and then open Debug tab.
Under Web Server setting, check the Enable SSL checkbox as shown below:
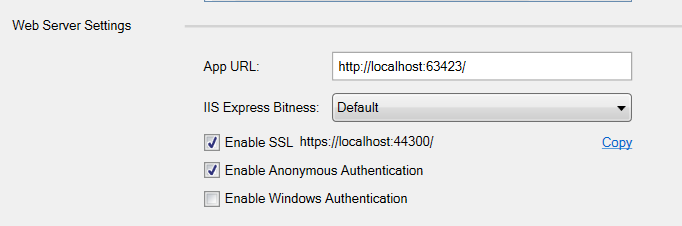
Note – You can find the source code of my sample application here.(sample does not include HSTS changes)
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
Sometimes just redirecting HTTP to HTTPS is not enough, so there is need of something which can instruct the browsers to always access the site via HTTPS.
What is HSTS?
- HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a web security policy mechanism which helps to protect websites against protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking
- It allows web servers to declare that web browsers (or other complying user agents) should only interact with it using secure HTTPS connections, and never via the insecure HTTP protocol
- Typically used only in non-dev scenarios
For example, when you try to access Google with http://www.google.com, the browser will give us 307 status code and will redirect http to https:
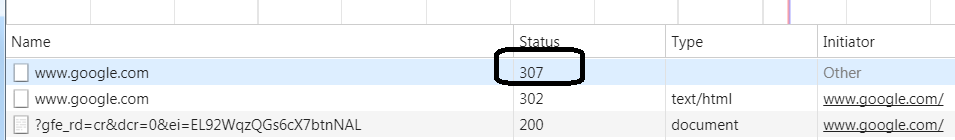
For this, we need to tell the application to send below header to the browser when the first time application hits the browser:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000
Important Note – The .Net team has announced HSTS middleware with .Net Core 2.1 that supports options for max age, subdomains, and the HSTS preload list. Currently, there are not any straightforward instructions on how to use this with .Net Core 2.1 so we will use NWebSec for HSTS.
We can add some code to the .Net Core application which will do above thing for us.
NWebseclets you configure quite a few security headers.
Add NWebsec.AspNetCore.Middleware from the Nuget:
Once the Nuget package is installed, add below line of code under Configure method:
app.UseHsts(h=> h.MaxAge(days:365)
Then, You need to submit your domain details on this site HSTS Preload site
and after that add preload as shown below:
app.UseHsts(h=> h.MaxAge(days:365).preload());
Important Note: Note that once you do this, the browser will refuse non-secure requests for your domain, so the only https version of your site will be called. But somehow if your site would not support https in the future then your site would not be accessed once you make above configuration with HSTS. Use it carefully.
Hope it helps.

Yury Sobolev is Full Stack Software Developer by passion and profession working on Microsoft ASP.NET Core. Also he has hands-on experience on working with Angular, Backbone, React, ASP.NET Core Web API, Restful Web Services, WCF, SQL Server.


