It’s like two children trying to buy a movie ticket by posing as adults in trench coats. (In case you weren’t aware, these kids did try it!) Even if a website claims to be encrypted, if you encounter a “Your connection is not private” error while trying to access it, the connection may not be.
Of course, the trick never really works, just like with those kids. Just like a good-natured box office clerk, your browser would laugh about it in the case of a website instead of issuing a dull warning message.
Nevertheless, it can be extremely harmful for both website visitors and backend administrators to ignore such a warning message. An open invitation to cybercriminals to monitor your website activity for their own nefarious purposes is given by an unencrypted connection, after all.
Don’t worry! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to successfully troubleshoot an SSL connection error whenever you encounter one. We’ll talk about the error message, the factors that led to its occurrence, and potential solutions for permanently removing it.
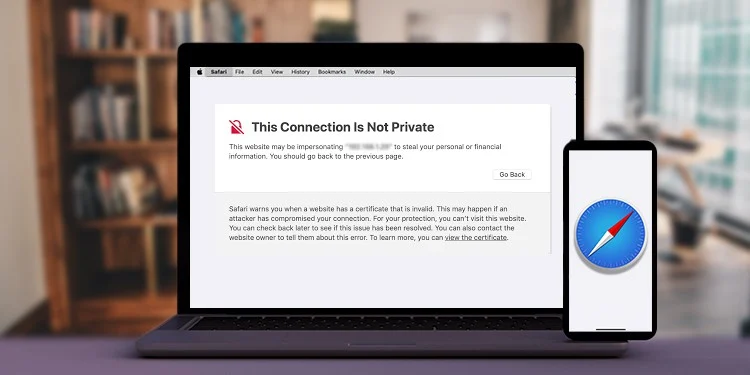
‘Your connection is not private’ Error: What Does It Mean?
Did the message “Your connection is not private” appear when you attempted to access a website? Don’t worry; your security is still intact and you are safe. You should still take this warning seriously, though, as continuing on the website might expose your device to cybersecurity threats.
Your browser checks the digital certificates installed on the server when you try to access a website to make sure it complies with privacy regulations and is secure before continuing. A browser such as Chrome or Firefox will prevent you from accessing the website with the message “Your connection is not private” if there is a problem with the certificate. Typical variants include:
- Google Chrome: “Your connection is not private. Attackers might be trying to steal your information from [website] (for example, passwords, messages, or credit cards).”
- Mozilla Firefox: “Your connection is not secure. The owner of [website] has configured their website improperly. To protect your information from being stolen, Firefox has not connected to this website.”
- Apple Safari: “Safari can’t verify the identity of the website [website]”
- Microsoft Edge: “Your connection isn’t private. Attackers might be trying to steal your information from [website] (for example, passwords, messages, or credit cards).”
- Internet Explorer: “There is a problem with this website’s security certificate.”
Digital certificates serve as the equivalent of online identity cards, proving that a website is who it claims to be. They do this by encrypting the connection between the client (your device) and the server (the website you’re trying to access), thereby helping to safeguard your personal information, passwords, and payment information.
So what should you do if you encounter this error while attempting to access a significant website? Fortunately, there are solutions to fix the issue and browse securely. While some are fairly simple and anyone can complete them, others call for assistance from the website administrator or even the hosting company.
Difference HTTP and HTTPS
Both the HTTP and HTTPS protocols are used to transfer data between various systems, such as your computer and a website. Since HTTPS is more secure than HTTP, that is the primary distinction between the two.
Since HTTP sends data in plain text, anyone can intercept it and read it. As a result, hackers can access sensitive data like passwords and credit card numbers. Contrarily, HTTPS uses encryption to safeguard your personal data, making it much more difficult for hackers to steal your data.
Your data is encrypted and verified using HTTPS using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security), ensuring its security and confidentiality. A padlock icon and a URL beginning with https:// denote a secure connection on websites that use HTTPS.
HTTPS is more secure than HTTP, but because encryption requires more processing power, it can also be a little slower. However, for transactions requiring the input of confidential information, HTTPS encryption is a requirement.
What is SSL Certificate, then?
Secure Sockets Layer, or SSL, is a technology that helps safeguard your internet connection and guards any private information you send or receive online.

Digital certificates known as SSLs are used to authenticate a website’s identity and create a secure connection between your device and the server that hosts the website. By doing this, you can be sure that any information you send or receive online is secure from hackers.
If a website has an SSL certificate, you’ll notice that the URL in your browser starts with “https” rather than “http” when you visit it. The address bar may also show a padlock icon next to the URL, which denotes that the website has a valid SSL certificate and that your connection is secure.
Your connection is protected by SSL certificates, which combine symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques. Data is encrypted and decrypted using a pair of keys called asymmetric encryption. This makes sure that the data can only be read by the intended recipient. On the other hand, symmetric encryption uses a single key that is shared by the sender and recipient to both encrypt and decrypt data.
There are various types of SSL certificates, ranging from the most basic to the most secure, depending on the degree of validation and protection required.
9 Possible Reasons for SSL Connection Errors
What, though, actually results in an SSL certificate error? SSL errors can occur on either the client or the server, which means they could be caused by either your computer or the website you’re attempting to access. To assist you in reducing your list of potential suspects, the following is a list of typical causes for the “Your connection is not private” error:
- Invalid Certificate:When a user’s browser encounters a self-signed certificate, an invalid SSL certificate, or when the certificate is otherwise not recognized by the user’s browser, the user’s browser will display an error message.
- SSL/TLS Protocol:A secure connection is created using the SSL/TLS protocol between a web server and a web browser. An error may be caused by problems with the protocol, such as out-of-date or unsupported versions.
- Intermediate Certificates:Between the SSL certificate and the root certificate, a chain of trust is established using intermediate certificates. If an intermediate certificate is absent or set up incorrectly, SSL errors may happen.
- Expired SSL:SSL certificates must be renewed on a regular basis because they have expiration dates. A secure connection can fail if an SSL certificate is invalid, expired, or revoked for any other reason.
- Antivirus Software:Some antivirus programs or browser add-ons can obstruct the validation of SSL certificates, resulting in errors.
- DNS Cache:Domain names are converted into IP addresses using DNS (Domain Name System). The error may be brought on by DNS cache problems, such as the cache storing outdated or inaccurate data.
- Wi-Fi Issues:There may be difficulties establishing a secure connection between the website and the client if the user’s Wi-Fi network has problems, such as a spotty or inconsistent connection. Public Wi-Fi networks are especially prone to these problems.
- Operating System:A connection error may occur if the user’s operating system, whether Windows or Mac, is outdated or contains corrupted files.
- Client-Side Errors:Client-side SSL errors may be brought on by problems with the user’s browser or security configurations, such as outdated or unsupported browser versions or incorrect SSL/TLS settings.
How to Fix ‘Your connection is not private’ Error
Nothing is more annoying for a website administrator than getting the “Your connection is not private” error message. It not only has the potential to decrease traffic, but it also poses a security risk to both your website and its users. Fortunately, there are a number of troubleshooting techniques you can use to fix this error and make sure your website is trustworthy and secure.
- Check Your SSL Certificate’s Expiration Date:SSL certificates must be renewed on a regular basis because they have expiration dates. An SSL error may occur if your SSL certificate has expired or is about to expire. Visit the SSL certificate section in your web hosting account or get in touch with your SSL certificate provider to find out when your SSL certificate expires.
- Confirm That the Certificate was Issued Properly:If the SSL certificate was not issued properly, an SSL error may happen. Verify that the SSL certificate was issued to the correct domain name and that the domain name is spelled correctly in the certificate in order to troubleshoot this issue. To confirm that all intermediate certificates have been installed correctly, you can also check the certificate chain.
- Run an SSL Server Test for Your Website:You can find out if your SSL certificate or server configuration problems are what’s causing the SSL error by running an SSL server test. Online, there are a number of free SSL scan tools available, including SSL Labs and Qualys SSL Server Test. These tools will check the SSL certificate and server configuration of your website and provide a thorough report of any problems discovered.
- Contact Your Web Hosting Provider for Support:If none of the aforementioned actions resolve the SSL error, there might be a problem with the server configuration at your web hosting company. Inform the support staff of your web hosting company of the error you are experiencing. To fix the problem, they might need to provide a new SSL certificate or update their server configuration.
The ‘Your connection is not private’ error’s common error codes
Digital certificates, security protocols, cryptographic algorithms, and network connections are just a few of the many causes of SSL errors. However, they also have a corresponding error code that website users and web administrators can use to further troubleshoot the problem. The meanings of some of those error codes are listed below, along with a list of them:
- ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID: This error occurs when the domain name on the SSL certificate does not match the domain name of the website you are trying to access.
- ERR_CERT_DATE_INVALID: This error occurs when the SSL certificate has expired or the date and time on your computer are incorrect.
- ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID: This error occurs when the SSL certificate is not issued by a trusted certificate authority.
- ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM: This error occurs when the SSL certificate uses a weak cryptographic algorithm that is no longer considered secure.
- ERR_CERTIFICATE_TRANSPARENCY_REQUIRED: This error occurs when the SSL certificate does not meet the Certificate Transparency policy requirements.
- ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH: This error occurs when the browser is unable to establish a secure connection due to a mismatch in the SSL/TLS version or cipher suite being used by the server and the browser.
- ERR_CONNECTION_CLOSED: This error occurs when the server terminates the connection unexpectedly.
- ERR_CONNECTION_RESET: This error occurs when the connection is reset by the server or your network.
- ERR_TIMED_OUT: This error occurs when the server does not respond within a certain time limit.
Contact Your Hosting Provider if You Still Experience the Issue
Sensitive data from your users, like login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal information, may be at risk if your website experiences a privacy error.
The first step you should take if an SSL connection error occurs on your website is to try to identify the problem on your own. Start by making sure the domain name matches the certificate, checking the certificate status, and making sure the certificate is current. To see if the error still occurs, you can also try clearing your browser’s cache or switching to another browser.
It is crucial that you contact your web host for assistance if you are unable to fix the SSL connection error. Your web host can direct you on how to fix the error and assist you in determining its root cause. To make sure that your website is secure, they might also be able to give you a fresh SSL certificate or assist you in configuring your server settings.
Give your web host as much information as you can when reporting an SSL connection error, including the error message, the URL of the impacted page, and any other pertinent information. This will hasten the process by which your hosting company will identify and fix the problem.

Javier is Content Specialist and also .NET developer. He writes helpful guides and articles, assist with other marketing and .NET community work



