Some of your unindexed sites may have the Google Search Console statuses “Not found (404)” and “Soft 404”. Despite having very similar names and the potential to seriously harm your SEO, these two problems are completely unrelated:
- Google cannot index your page in the case of “Not found (404)” because it returns a 404 HTTP response code because its content is missing,
- Google is perplexed by your page in the “Soft 404” scenario. Even though your server says the page is online, its content is missing.
The way you handle “Not found (404)” and “Soft 404” pages could be crucial to your indexing strategy, user experience, and crawl budget optimization.
Let’s explore their differences further and learn how to address them.
What does the “Not found (404)” status actually mean?
When “Not found (404)” appears in Google Search Console’s Page indexing (Index Coverage) report, it means one of the following:
- Googlebot communicated with your server to retrieve a given page,
- The server couldn’t find the requested URL, so it responded with the 404 HTTP response code.
Servers communicate with crawlers and browsers through status codes. The server most likely returns the 200 status code to your browser whenever you can access a page without any issues.
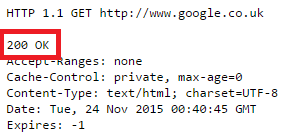
There are also many status codes referring to possible errors, because of which the server cannot grant you access to a page. The 404 status code is one of them. It indicates that the page is unavailable as a result of the server’s failure to locate it.
Google doesn’t index 404 pages because they present no value to users.
What Causes “Not found (404)” in Google Search Console?
However, the possible reasons why the server responds with the 404 status code may differ:
Removing a Page
When managing a website, it’s possible to unintentionally delete a page. If it’s a crucial page with many links pointing to it, it may contribute to a significant traffic loss for your website.
But you may also want to remove your content on purpose.
There are a few explanations as to why you might want to do that:
- Optimizing duplicate content that is useless to your users and business but which you don’t want to change.
- Possessing orphan pages that do not attract traffic to your website but cannot be linked to or redirected.
- Addressing the out-of-stock product pages that aren’t bringing people back to your website and no longer have search demand or backlinks.
- Concealing information that you mistakenly published on the production site, such as during a website move.
Removing a page from your website that doesn’t add to its commercial worth or could damage its SEO is perfectly acceptable.
And if there is no other way to solve your problems (such as by changing or redirecting your content), feel free to put up the 404 status code.
Changing the URL structure
Given how frequently your website is updated, it is common for some URL addresses to change over time.
However keep in mind that if a page’s link is broken, the server won’t deliver the requested information to visitors since it can’t find the page.
Another instance is when you manually add links or type into a certain website and make a typo in the URL.
Such mistakes may concern, e.g.,
- words with alternate spellings (optimisation vs. optimization) or
- adding spaces to a URL as they will be replaced by the %20 string (example.com/red-%20car)
You might think the modification is unimportant. Yet, even a small change in the URL address is taken as a new URL by search engine algorithms.
How do 404 errors impact SEO?
Although some “Not found (404)” pages are unavoidable, leaving them unoptimized could lead to additional problems with your website.
Negative user experience
Users weren’t likely looking for a blank page when they typed in your “Not found (404)” URL, regardless of how they did it.
Seeing no content on a target page may create a negative user experience. Also, your conversion rates are strongly impacted by how people perceive your website.
Hence, you must make sure that your website’s 404 pages don’t make your visitors feel lost.
Making a personalized 404 page that not only looks excellent but also educates users is a fantastic idea
- Why they see the “Not found (404)” page, and
- What further actions they may take on your website, e.g., read your top articles.
Even when consumers can’t access the exact page they want to, by designing a strong 404 page, you may persuade them to continue using your website.
Wasting your crawl budget
The resources required for Google to crawl the entire Web are finite.
Bots may never reach the more important pages on your website before your crawl budget is wasted if they are allowed to freely crawl your “Not found (404)” pages.
Crawl budget optimization services can help you unlock the full crawling potential of your website if you believe that might be the case.
Diminishing your traffic potential and ranking signals
If you have many internal and external links pointing to your 404 pages, the accumulated PageRank goes to waste.
How to troubleshoot “Not found (404)”
Go through the list of impacted pages in the Page indexing (Index Coverage) report first to see if they are a result of your choice.
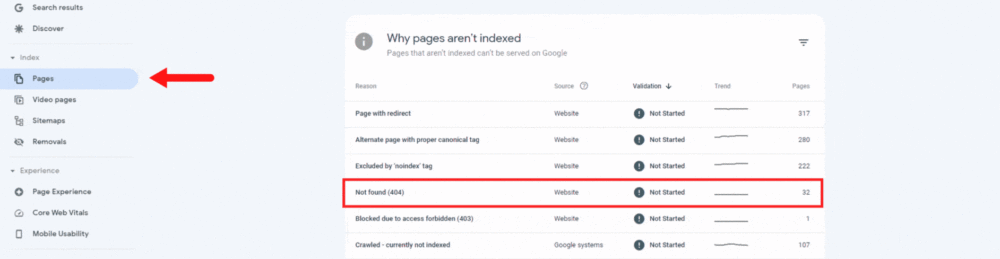
Also, if you run a big website, using an SEO crawler like Screaming Frog or WebSite Auditor makes it easy to navigate your 404 pages.
Make sure your XML sitemap doesn’t contain any “Not found (404)” pages as another thing to double-check. On the status screen, you can filter your affected URLs by selecting “All submitted pages” in the upper left corner.
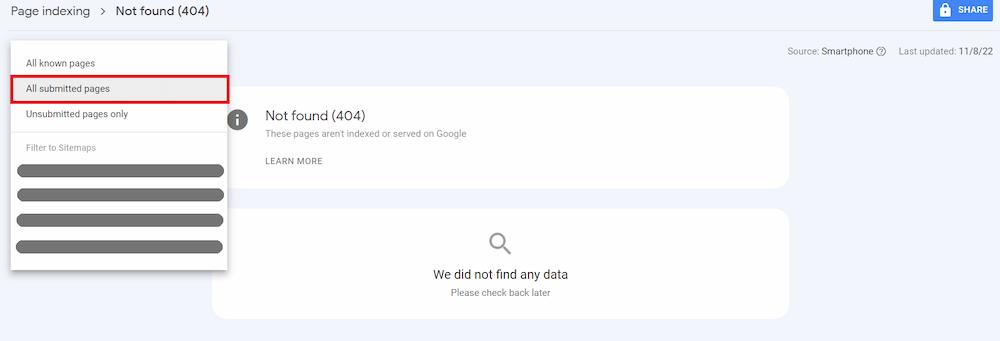
Ideally, you shouldn’t see any URLs on the list of “All submitted pages” (or, as it was in the past, within the “Submitted URL Not found (404)” status), as your sitemap file should only contain pages responding with the 200 status code.
If not, it could signify any of the following:
- You don’t want the page to be indexed any longer – you removed a submitted page but didn’t update the sitemap file, or you updated your sitemap, but it contains the error page anyway.
Every time you make changes on your end, make sure to update your sitemaps.
Furthermore keep in mind that even if you make changes, they might not be adopted right away. After Google crawls your sitemap again, check your “All submitted pages” report once again.
- You want the page to be indexed – you added your page to the sitemap but then removed the URL by mistake.
- There are URLs in your sitemap that you don’t care to get indexed. In this situation, avoid wasting your crawl budget by establishing XML sitemaps according to best practices for SEO.
Set up 301 redirects
If any of the following apply to your “Not found (404)” page:
- Shifted your content to a semantically related page,
- Removed your page but have another relevant page on your website that you want readers to go to,
- Removed the page that generated traffic previously or is currently being searched for using the keywords it targets, and
- Have numerous internal and external links going to your “Not found (404)” in order to surpass the authority of a certain page.
In a perfect world, the “Not found (404)” page would alter its status in Google Search Console to “Page with redirect” following the correct redirect (and after Google re-crawled the URL).
But, keep in mind that you shouldn’t hurriedly redirect your “Not found (404)” pages to irrelevant context-free URLs just for redirecting’s sake. If not, it can contribute to other problems with your website, such as the “Soft 404” error we’ll cover later.
Monitor internal and external linking
Make sure a specific page isn’t heavily linked throughout your website and from outside sources when you believe it shouldn’t exist and should instead be returning the 404 HTTP status code.
You can substitute links to related pages that return a status code of 200 for internal links to 404 pages.
When it comes to external linking, you can get in touch with the websites that are linked to you and request that they update any outdated links. I realize that’s not always practical, particularly if your page has a large number of backlinks.
In this situation, either put up the 410 HTTP status code or perform a 301 redirect to an existing page (or think about building new related content you may redirect to).
What does the “Soft 404” status actually mean?
When the server returns the 404 error, soft 404 is not generated. When a page meets the following two criteria, Google classifies it as a soft 404:
- Although it appears that their content is missing, the server still returns a 200 status code in response.
- In other words, Google feels that a given Site should return the 404 status code despite returning a 200 answer. It deduces that the page shouldn’t be indexed on the basis of this.
How Do I Fix “Soft 404” errors in Google Search Console?
Your pages that are “Soft 404” affected can be found in the Page Indexing report. It is simple to reach via the Google Search Console’s left navigation bar.
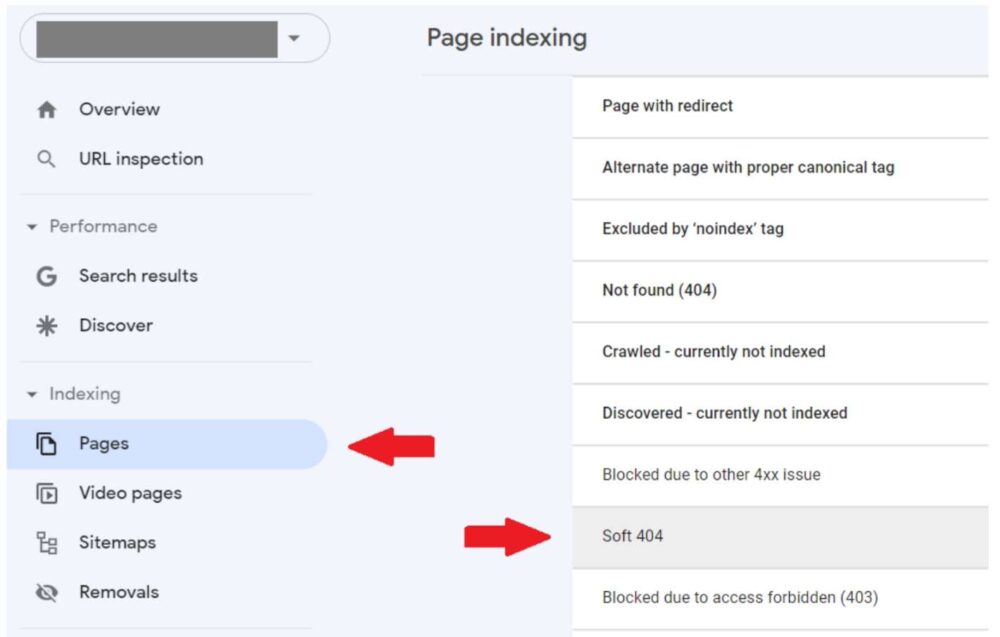
By clicking on the status name, you can learn more about those sites. A list of URLs and a graph illustrating the evolution of the number of impacted pages are displayed. You can export the list using the button located in the upper right corner.
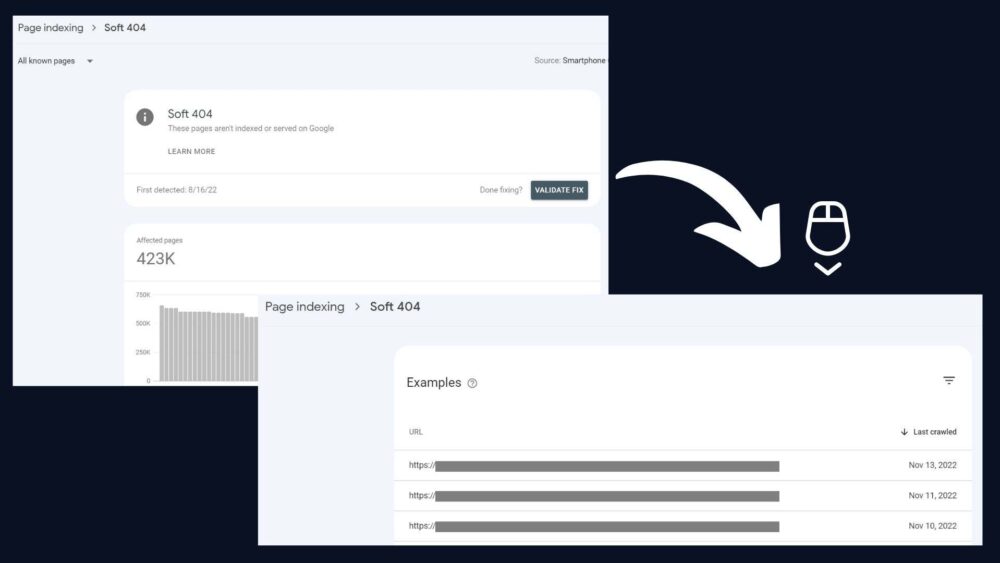
According to what John Mueller said on SEO Office Hours in July 2021, Google Search Console reports only those soft 404 pages that are considered as such on mobile. If some desktop pages are labeled as soft 404, but their mobile versions aren’t affected by the problem, you may not be able to see them in GSC.
Let me walk you through the potential causes and solutions for the “Soft 404” status.
Ensure that non-existing pages return a 404 status code
Many websites offer unique 404 pages that, rather than just stating the problem, guide readers to the data they require and entice them to explore the domain. These websites provide a 200 HTTP status code when the process becomes untidy as a result of being left unchecked.
Because empty 200 pages squander Google’s crawl budget, it’s detrimental for your SEO. Setting up your server to produce the appropriate status code for customized pages that don’t exist can solve this issue. Not Found, 404.
Avoid redirecting to irrelevant pages
You could be tempted to route all of the obsolete or empty pages to one central location, like your home page, when faced with a large number of them. Yet from the viewpoint of the people that visit your website, this method is useless.
Google may classify this kind of redirect as a soft 404 when it occurs. Adhere to stricter guidelines when building redirects to address this issue:
A 404 page should be set up in place of a redirect when you can’t discover another page that fits the user’s intent. Make your redirects thematically related.
Avoid pages with little or no content
An eCommerce website with products that often move in and out of stock is a good example of a page with little to no content. Google will probably label it as a soft 404.
Your users won’t benefit from thin content pages, and they can harm your SEO. Examples include:
- Wasting your crawl budget,
- Convincing Google that your whole website lacks quality, which may discourage Google from crawling your website as often,
- Lower rankings following a thin content manual action.
Using the noindex meta tag is the best way to stop search engines from indexing pages with little to no content. Reviewing your site architecture is a fantastic idea as well as figuring out which product categories are unnecessary and don’t serve a function.
Be careful of 404-like words
Because Google’s algorithms aren’t flawless, they could mistakenly classify a page if it contains phrases that are typically found on a 404 page. When a product page on an e-commerce website, for instance, uses phrases like:
- “out of stock,”
- “product unavailable,”
- “we don’t deliver to your location.”
You can try to troubleshoot the “Soft 404” status by deleting those words or using neutral synonyms.
Fix your rendering issues
Google might not be able to display some material because it couldn’t render it. When your robots.txt file forbids crawlers from accessing CSS or JavaScript files, such issues usually arise.
By reviewing your pages with the URL Inspection Tool, you may determine whether Google delivers them appropriately. Simply click the magnifying glass icon next to the URL you’ve chosen from the “Soft 404” list.
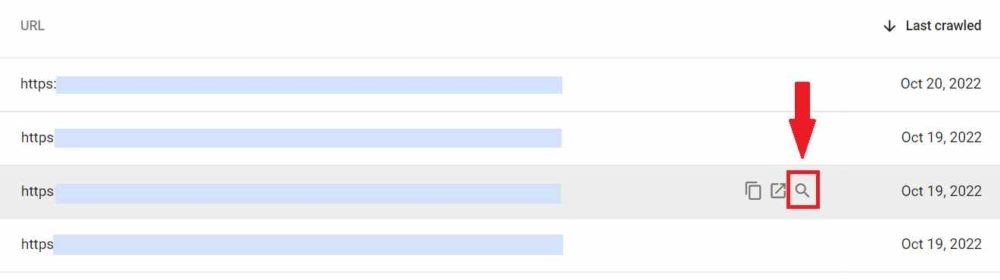
Make sure Google has access to the rendering-related resources in order to solve the issue. Check your robots.txt file to ensure that CSS and JavaScript crawling is permitted.
Conclusion
To troubleshoot the “Soft 404” status in Google Search Console, try:
- Checking if your non-existent pages correctly return the 404 status code,
- Fixing your irrelevant redirects,
- Marking your thin content pages with the noindex tag,
- Deleting words that may be misleading for Google,
- Getting your rendering SEO in check.
These are effective solutions to the 404 error and the soft 404 issues, but none of them guarantee lasting results.
Get your ASP.NET hosting as low as $1.00/month with ASPHostPortal. Our fully featured hosting already includes
- Easy setup
- 24/7/365 technical support
- Top level speed and security
- Super cache server performance to increase your website speed
- Top 9 data centers across the world that you can choose.

Yury Sobolev is Full Stack Software Developer by passion and profession working on Microsoft ASP.NET Core. Also he has hands-on experience on working with Angular, Backbone, React, ASP.NET Core Web API, Restful Web Services, WCF, SQL Server.



